Roller Bearings
-

Cylindrical Roller Bearings
n bearings of this type, the cylindrical rollers are in linear contact with the raceways. They have a high radial load capacity and are suitable for high speeds.
There are different types designated as NU, NJ, NUP, N, NF (for single-row bearings), NNU, and NN (for double-row bearings depending on the design or absence of side ribs).
The outer and inner rings of all types are separable.
Some cylindrical roller bearings have no ribs on either the inner or outer ring, so the rings can move axially relative to each other. These can be used as free-end bearings. Cylindrical roller bearings, in which either the inner or outer rings has two ribs and the other ring has one, are capable of taking some axial load in one direction Double-row cylindrical roller bearings have high radial rigidity and are used primarily for precision machine tools.
Pressed steel or machined brass cages are generally used, but sometimes molded polyamide cages are also used.
Depending on the existence of ribs on their rings, Cylindrical Roller Bearings are classified into the following types:
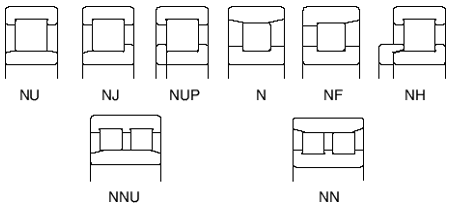
Types NU, N, NNU, and NN are suitable as free-end bearings. Types NJ and NF can sustain limited axial loads in one direction. Types NH and NUP can be used as fixed-end bearings. NH-type cylindrical roller bearings consist of the NJ-type cylindrical roller bearings and HJ-type L-shaped thrust collars.
The inner ring loose rib of an NUP-type cylindrical roller bearing should be mounted so that the marked side is on the outside. -
Tapered Roller Bearings

Bearings of this type use conical rollers guided by a back-face rib on the cone. These bearings are capable of taking high radial loads and axial loads in one direction.
In the HR series, the rollers are increased in both size and number giving it an even higher load capacity. They are generally mounted in pairs in a manner similar to single-row angular contact ball bearings. In this case, the proper internal clearance can be obtained by adjusting the axial distance between the cones or cups of the two opposed bearings. Since they are separable, the cone assemblies and cups can be mounted independently.
Depending upon the contact angle, tapered roller bearings are divided into three types; normal angle, medium angle, and steep angle.
Double-row and four-row tapered roller bearings are also available. Pressed steel cages are generally used. -

Spherical Roller Bearings
Shown in the figures, types EA, C, CD, CA, which are designed for high load capacity, are available. Types EA, C, and CD have pressed steel cages; and type CA has machined brass cages. Type EA has especially high load capacity, features low torque, and has a high-strength cage.
An oil groove and holes are provided in the outer ring to supply lubricant and the bearing numbers are suffixed with E4.
To use bearings with oil grooves and holes, it is recommended to provide an oil groove in the housing bore, since the depth of the groove in the bearing is limited. -
Thrust Roller Bearings

Available with cylindrical or spherical rollers, NSK's thrust roller bearings sustain only axial loads, but they are suitable for heavy loads and have high axial rigidity. Spherical thrust roller bearings contain convex rollers and have a self- aligning capability and are free of any influence of mounting error or shaft deflection. Standard cages are machined brass, where the E-type offers a pressed cage for high load capacity.
-

Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are a bearing that is classified as either radial or thrust depending on the direction of the load being supported. Needle roller bearings include bearings whose rollers slightly exceed the size range of needle rollers as stipulated by ISO. Needle roller bearings include drawn cup and solid radial bearings, as well as application-specific cam followers, and roller followers. Thrust bearings include thrust needle bearings.
